In a world where Mother Nature can throw a tantrum at any moment, resilient architecture stands as the superhero of the building world. It’s not just about creating pretty structures; it’s about crafting spaces that can withstand the test of time and the occasional hurricane. Think of it as giving buildings a gym membership—stronger foundations, flexible designs, and a workout routine that keeps them standing tall when the going gets tough.
Imagine a house that doesn’t just shrug off storms but also adapts to its environment, like a chameleon with a flair for modern design. Resilient architecture combines innovation and practicality, ensuring that homes and communities thrive even in the face of adversity. As climate change looms, this approach isn’t just smart; it’s essential. Let’s dive into the world of buildings that laugh in the face of disaster and keep our communities safe and stylish.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Resilient Architecture
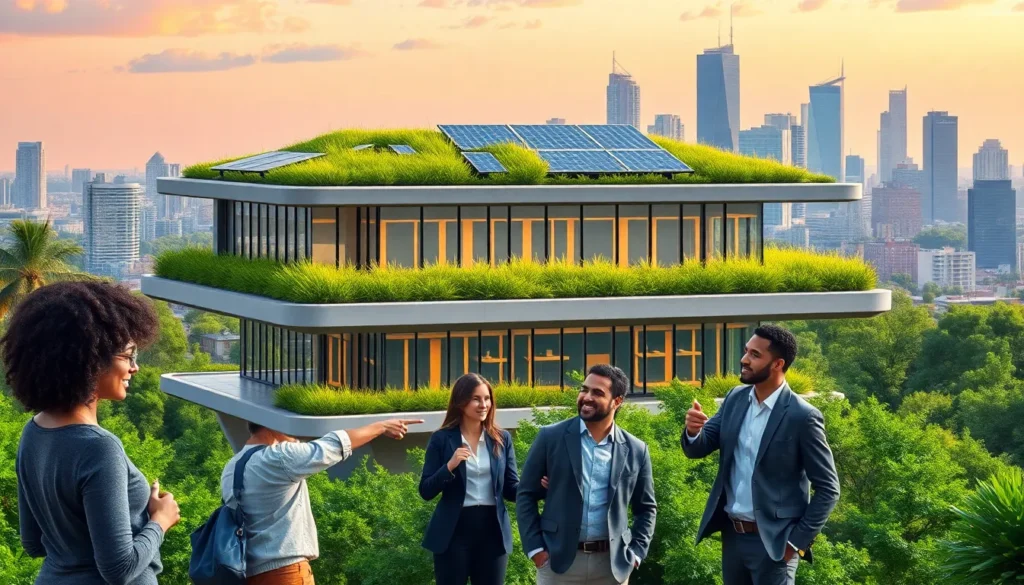
Resilient architecture focuses on designing structures that withstand natural disasters and climate change impacts. This design approach integrates techniques that allow buildings to adapt to extreme weather, seismic events, and other environmental stresses.
Understanding the key principles of resilient architecture helps communities prepare for unforeseen challenges. These principles emphasize durability, flexibility, and efficiency in resource use. Structures should incorporate robust materials, innovative engineering techniques, and smart technology to enhance resilience.
Adaptation strategies play a vital role in this field. For instance, elevated structures in flood-prone areas significantly reduce damage risks. Green roofs improve insulation and manage stormwater effectively, demonstrating multifunctional design.
Designing for resilience does not sacrifice aesthetics. Architects create visually appealing structures while ensuring functional integrity. This balance can improve community pride and attract investment, proving the economic benefits of resilient design.
The integration of renewable energy sources further enhances resilience. Solar panels and wind turbines provide power during disruptions, ensuring that communities remain operational. Such energy independence signifies a crucial element of resilient architecture.
Current trends highlight the importance of community involvement in resilient design processes. Engaging local residents fosters a sense of ownership and accelerates the identification of particular needs. These collaborative efforts result in tailored solutions that reflect the unique characteristics of each community.
Embracing resilient architecture ensures that future generations inhabit safer, more sustainable environments. As the frequency and intensity of climate-related events increase, prioritizing resilience in building design becomes essential.
Key Principles of Resilient Architecture
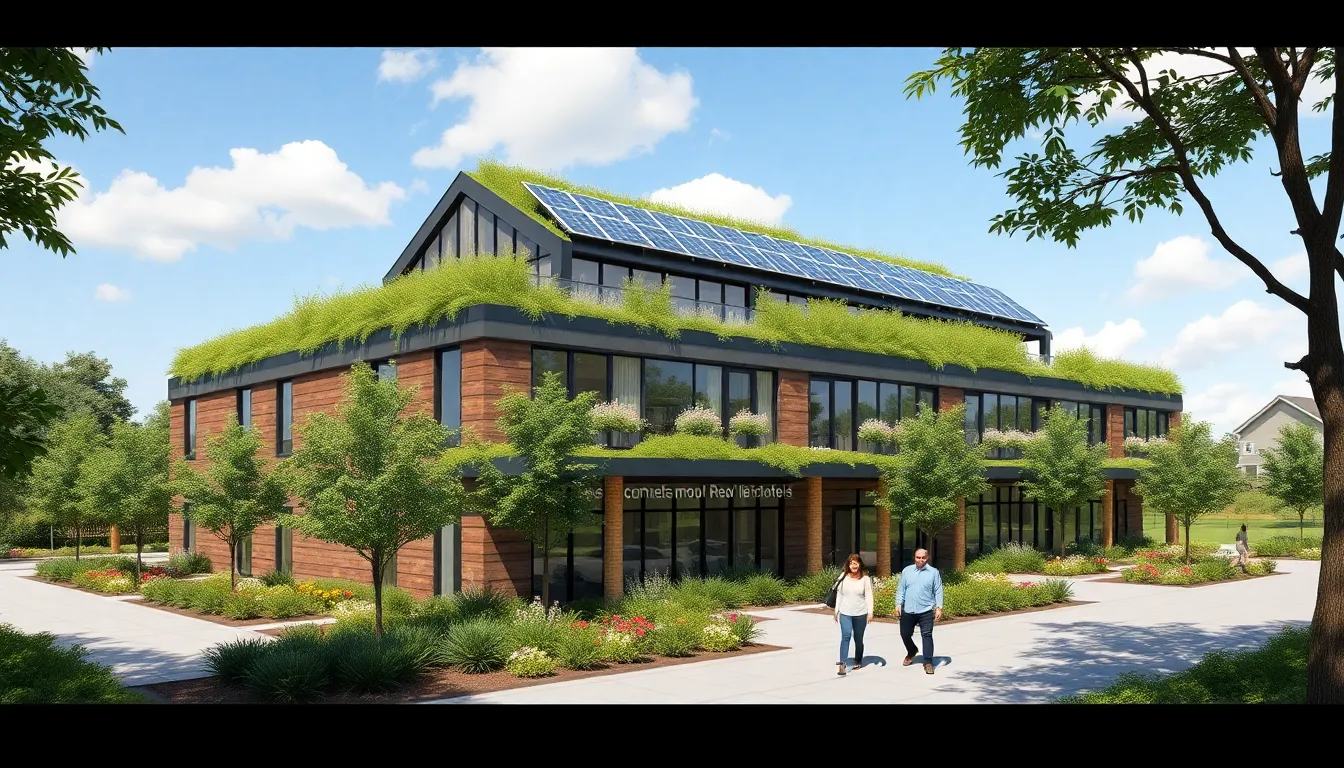

Resilient architecture is grounded in several key principles that enhance building performance amid challenges. These principles include sustainability, adaptability, and efficiency.
Sustainability
Sustainability emphasizes minimizing the environmental impact of construction. Prioritizing renewable materials reduces waste and conserves energy. Implementing green roofs and permeable pavements further promotes ecological balance. Structures designed with rainwater harvesting capabilities can enhance water conservation. Long-lasting building materials also contribute to sustainability, ensuring minimal maintenance over time. Many architects integrate solar panels into designs, promoting energy independence while addressing climate change.
Adaptability
Adaptability refers to the ability of buildings to respond to changing conditions. Flexibility in design allows spaces to accommodate various functions over time. Resilient structures often feature movable walls or multi-use areas to maximize utility. Incorporating modular design elements facilitates easy expansion or reconfiguration as community needs evolve. Adjusting to local environmental conditions, such as elevating buildings in flood-prone areas, enhances safety. The objective is to create spaces that maintain usability despite unforeseen challenges.
Efficiency
Efficiency focuses on optimizing resources throughout the building lifecycle. Streamlined construction methods reduce waste and lower costs. Implementing energy-efficient systems, such as advanced insulation and smart technologies, enhances overall performance. Effective resource management minimizes electricity and water consumption, leading to sustainable operational practices. Buildings achieving LEED certification demonstrate a commitment to efficiency, resulting in lower long-term operational costs. Ultimately, fostering an environment of efficiency benefits both occupants and the surrounding community.
Examples of Resilient Architecture
Resilient architecture manifests in various notable projects and innovative designs tailored to withstand environmental challenges.
Notable Projects
One example is the Bosco Verticale in Milan, Italy. This pair of residential towers features over 9,000 trees and 20,000 plants, promoting biodiversity and air quality. Another prominent project is the Jinshan Sports Center in Shanghai, designed to endure typhoons. Its aerodynamic shape reduces wind resistance, showcasing adaptability to extreme weather. The Spheres in Seattle provide a unique indoor botanical garden, enhancing urban resilience by integrating greenery into architecture. Each of these projects demonstrates how resilient structures can harmonize with their surroundings while addressing climate-related risks.
Innovative Designs
In resilient architecture, innovative designs play a key role. Elevated buildings in flood-prone regions utilize stilts to minimize water damage. Green roofs capture rainwater and improve insulation, contributing to energy efficiency. Modular construction methods enable quick adjustments and minimize waste during the building process. Buildings like the Bullitt Center in Seattle utilize rainwater harvesting alongside solar energy, showcasing sustainability and energy independence. Architects increasingly focus on passive design strategies, optimizing natural light and ventilation without relying on mechanical systems. These innovative approaches redefine how structures respond to environmental challenges.
Benefits of Resilient Architecture
Resilient architecture offers numerous advantages that enhance the longevity and safety of buildings. Durability stands at the forefront, providing structures that withstand harsh weather and natural disasters. According to the National Institute of Building Sciences, buildings designed with resilience in mind can significantly reduce economic losses during extreme weather events.
Flexibility plays a crucial role as well. Spaces that adapt to changing needs contribute to sustainable living environments. They allow for reconfiguration as community requirements evolve over time, fostering a dynamic relationship between architecture and its users.
Energy efficiency stays another vital benefit. Incorporating energy-efficient systems reduces operational costs and ensures reliable energy access during unforeseen disruptions. For instance, structures equipped with solar panels can generate power when traditional sources become unavailable.
Sustainability contributes to both environmental preservation and community well-being. Resilient buildings often utilize renewable resources, such as reclaimed materials, which minimize waste and support local economies. The integration of green roofs and rainwater harvesting systems illustrates how these techniques promote ecological balance.
Community engagement enhances the design process, reflecting local culture and identity. Involving citizens in architectural decisions creates a sense of ownership and pride, fostering a stronger community connection. Examples like the Bosco Verticale and Jinshan Sports Center showcase how resilient architecture contributes to social cohesion.
Innovative construction methods also play a part in minimizing environmental impact. Techniques such as modular construction reduce waste and streamline building processes, ultimately lessening the carbon footprint.
In essence, resilient architecture provides effective solutions for contemporary challenges. The proactive design of buildings not only addresses immediate safety concerns but also prioritizes sustainability and efficiency, setting the standard for the future of architecture.
Future Trends in Resilient Architecture
Emerging trends in resilient architecture focus on innovative design solutions. Biophilic design, which incorporates natural elements into buildings, enhances occupant well-being while promoting sustainability. Increased use of artificial intelligence in structural analysis leads to optimized designs that can withstand extreme weather conditions.
Smart buildings equipped with advanced sensors monitor environmental changes, adjusting systems in real time. Modular construction techniques facilitate faster assembly and disassembly, allowing for quick adaptations in response to climate events. Drone technology assists in surveying and inspecting buildings, ensuring they meet resilience standards.
Inclusivity in the design process fosters community engagement. Stakeholder involvement results in structures reflecting local needs and cultural identities. Resilient communities arise from this collaborative approach, with shared spaces designed to accommodate diverse populations during emergencies.
Sustainable materials are gaining traction in resilient architecture. These materials focus on reducing environmental impact while enhancing durability. Recycled content in construction and local sourcing minimize carbon footprints.
Energy independence continues as a priority. Integration of renewable energy sources ensures buildings remain operational during disruptions. Solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems play critical roles in creating self-sustaining structures.
Climate-responsive design strategies improve resilience against temperature extremes and flooding. Buildings designed with operable windows, green roofs, and rainwater harvesting systems contribute to energy efficiency and environmental stewardship.
As resilient architecture evolves, a commitment to these trends will shape the future of urban planning. Adaptability and sustainability remain at the forefront, ensuring communities thrive in an ever-changing environment.
Resilient architecture stands as a vital response to the challenges posed by climate change and natural disasters. By emphasizing durability and adaptability, architects can create structures that not only protect but also inspire communities. The integration of sustainable practices and innovative design solutions ensures that buildings remain functional and aesthetically pleasing, even in the face of adversity.
As the focus on community involvement grows, the potential for tailored architectural solutions increases. This approach fosters a sense of ownership and pride among residents. Embracing resilient architecture is essential for crafting a sustainable future where communities can thrive amidst uncertainty.